Build a manganese concentration plant can improve the utilization rate of manganese ore resources and meet the market demand for manganese concentrate. Manganese ore can be processed into manganese concentrate, which is widely used in steelmaking, batteries, chemicals, and other fields. Global environmental protection requirements for manganese plants are becoming increasingly stringent. Therefore, the construction of a manganese plant must take many factors into account. Its core goal is to achieve efficient, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective manganese ore beneficiation and processing.
Use the table of contents below to navigate through the guide:
01Preliminary Preparation for Build a Manganese Concentration Plant
1. Resource Assessment and Feasibility Analysis
In the early stages of building a manganese concentrator, the manganese ore
resources should be evaluated. First, the quality of the manganese ore should be
analyzed, including the grade of the raw ore, mineral composition (such as
manganese oxide or manganese carbonate), and
impurity content. Then, the manganese ore reserves and mining conditions should
be assessed, including the scale of the ore body, burial depth, and the mining
method to be adopted — either open-pit mining or underground mining.
A feasibility analysis report should be prepared based on the above
evaluation results. The report should include technical feasibility, economic
benefit forecasts, and the investment payback period.
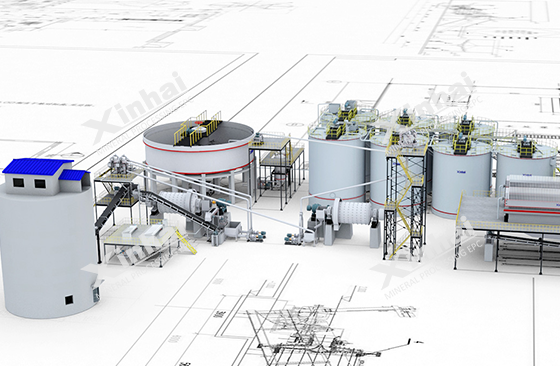
2. Site Selection and Environmental Impact Assessment
The site selection for a manganese concentrator is particularly important. To
reduce transportation costs, it is recommended to build the plant close to the
mining area. Natural conditions such as geology, hydrology, and meteorology must
be fully considered, along with the provision of essential infrastructure,
including transportation, power supply, and water supply and drainage
systems.
An Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) must be conducted to determine
wastewater and waste residue treatment plans and to formulate ecological
protection measures. In addition, it is necessary to obtain permits such as
mining licenses, land-use approvals, and EIA approvals.
02Manganese Concentration Plant Process Design
1. Beneficiation Test and Process Design
The first step is to conduct beneficiation tests on the manganese ore, which
include ore sampling and preparation, studies of the ore’s physical and chemical
properties, and process flow testing.
Following the test results and site planning, the process flow and equipment
layout for the manganese concentrator are designed. Common manganese ore
beneficiation methods include gravity separation (using jigs and shaking
tables), magnetic separation (either strong or weak magnetic separation),
leaching, and roasting reduction. However, it is difficult to achieve ideal
impurity removal and manganese enrichment with a single beneficiation method.
Therefore, most manganese beneficiation processes adopt a combined approach,
such as "crushing–grinding–magnetic separation–gravity separation."
2. Key Euipment Selection
Key Equipment
The key equipment includes: Crushing equipment(jaw crusher, cone
crusher).Grinding equipment(ball mill, rod mill).Separation equipment(magnetic
separator, flotation cells, spiral
chute).Dewatering equipment(thickener, filter)

Equipment Selection Principles
Equipment models should be selected based on a comprehensive consideration of
process design, site area, planned production capacity, and equipment handling
capabilities.
3.Tailings Treatment and Automation Technology
To better implement environmental protection strategies, tailings produced
after beneficiation must undergo dewatering treatment. A commonly used method is
tailings dry stacking, which reduces the moisture content of
the tailings using equipment such as thickeners, filter
presses, and dewatering screens. For flotation tailings, special attention
should be given to removing residual reagents. The final tailings should be
transported to a tailings storage facility.
Modern manganese concentrators should make full use of automation
technologies such as DCS control systems and AI monitoring systems. These
technologies not only help reduce labor costs but also ensure real-time,
accurate monitoring of each process stage.
03Construction and Equipment Installation for Manganese Concentration
Plant
1. Site Preparation
In the early stages of concentrator construction, comprehensive site leveling
operations must be carried out. This is a critical prerequisite for the smooth
progress of subsequent infrastructure development. The construction team should
use heavy machinery such as bulldozers and excavators to perform earthwork
balancing according to design specifications, clear surface vegetation and
obstacles, and ensure that the site slope meets drainage requirements. For
special geological areas, localized reinforcement may be necessary to form a
flat, solid, and well-drained construction base.

2. Infrastructure Development
Simultaneously, necessary infrastructure construction should proceed,
including standardized steel-structured beneficiation plants, raw material and
finished product warehouses, administrative buildings equipped with modern
office facilities, dormitory areas to meet employee living needs, and supporting
amenities such as canteens and bathhouses.
3. Equipment Installation and Commissioning
A scientifically rigorous construction plan should be formulated for
equipment installation, clearly defining timelines, resource allocation, and
construction requirements for each stage. A comprehensive safety management
system should be established, with dedicated safety officers supervising
construction activities to ensure a safe, controlled, and high-quality
installation process. After installation, equipment must undergo trial runs and
commissioning to ensure smooth production startup.
04Operation and Management of Manganese Concentration Plant
1.Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Strict SOPs should be established for production management, covering all
stages such as ore crushing, grinding, separation, and dewatering. These
procedures should define equipment operation parameters, maintenance schedules,
and contingency plans for anomalies. Regular training and assessments must be
conducted to ensure staff compliance with SOPs.

2.Quality Control
Dynamic monitoring of manganese concentrate grade is essential. Techniques
such as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) or chemical analysis should be
used to test manganese content and impurities (such as iron, silicon, and
phosphorus). Based on test results, process parameters (such as magnetic
separation intensity and reagent dosage) should be optimized to ensure the
concentrate meets contract requirements (typically Mn ≥ 30%). A quality
traceability system should be established to analyze the causes of nonconforming
products and provide feedback to the production line, forming a closed-loop
management system.
Conclusion
The above outlines the construction process of a manganese concentrator and
its operational management after commissioning.
Xinhai Mineral Processing offers a full industry chain service
(EPC+M+O) for mining, plant construction, equipment
manufacturing and installation, and plant operation.
If you are planning to build a manganese concentration plant, partner with Xinhai to
ensure efficient, reliable, and profitable project success. Contact us today to
start your journey!


 marketing@ytxinhai.com
marketing@ytxinhai.com  0086 13810327080
0086 13810327080 






































































































 CHAT
CHAT MESSAGE
MESSAGE







