For decades, the heap leaching process has developed rapidly with the technical progress and innovation, and a lot of experience and knowledge have been accumulated in the design. It has the advantages of small investment, low cost, short construction time and less production, so it has been widely spread in the world. Next, we will introduce the gold heap leaching process to you by combining the process features.
IntroductionCrush the low-grade gold ore to a certain size (or granulation), pack them in the leakproof bottom mat which is paved with asphalt, concrete or plastic materials, then use the low concentration of cyanide, alkaline solution, and non-toxic solvent or sulfuric acid solution to spray the ore heap, dissolving the gold. The gold-bearing solution filter from the ore heap, and then adopt activated carbon adsorption or the zinc powder exchange precipitation to recycle the gold.
In short
 Process flow
Process flow Flowsheet of Xinhai heap leaching process
Flowsheet of Xinhai heap leaching process1. Raw ore treatment
Crush the raw ore to a certain level (30-50mm), then directly send them to heap leaching;
Or carry out the granulating process (the finer particles reunite into coarse particles), then the ore is transported to the heap through the forklift truck.
So here comes the question!
Many people might wonder, why we would crush the ore then carry out granulation to increase the volume?
What is the purpose of the crushing? It is to expose the gold particles from the ore, and then fully react with the cyanide solution in the later steps. The same goes for grinding, both are to guarantee the sufficient dissociation of the gold particles.
Isn't the powder more suitable for infiltration? Why do we need granulation?
1) It is easy to appear channeling in the heap leaching process of ungranulated ore, namely the permeability is not so good, and the cyanide solution totally runs away without sufficiently reacting with the ore.
2) In addition, when stacking the granulation ore, we can avoid the migration of the powder ore, which ensures the stability of the heap ore.
In fact, whether granulate or not, each has its advantages. In the actual design, we need specific experiment to know which way is more suitable for the customer's mine plant.
2. Spray system
Set up the spray system in the ore heap. After the cyanide solution reacts with ore heap, the gold-bearing solution filters from the bottom of the ore heap, and flows into the pregnant solution pool, then push them to the adsorption column by the pump. The solution after activated carbon adsorption is the barren solution, and it can return to the spray system for recycling.
The leaching process is divided into spray leaching and dripping leaching.
Spray leaching: the nozzle sprays the solution (sent by the piping system) to the air, which forms the raining effect then scatters the space of the ore heap.

The dripping leaching system on the customer's spot is similar to the dripping device that used in plant irrigation, which falls down within a short distance and small area.
It is easier for the cyanide contained in gold leaching solvent to diffuse into the air, which can cause environmental pollution. So the dripping leaching is more widely used.
3. Desorption electrolysis
After the activated carbon adsorption, the gold solution is sent to the disruptions electrolysis system for separation.
Heap leaching and CIP processBoth heap leaching process and CIP process use the cyanide reagent, so, what is the difference between the two?
* Same functional mechanism
4Au+8NaCN+O2+2H2O→4Na[Au(CN)2]+4NaOH* Different application pattern
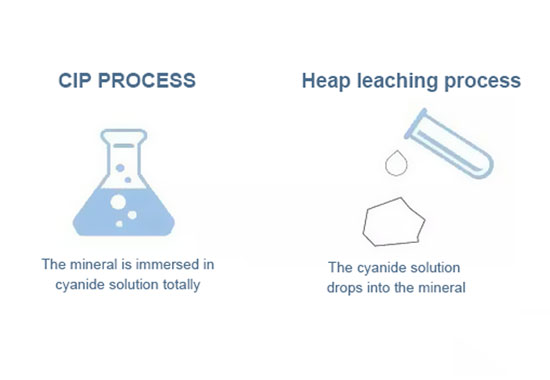
In the same mine, CIP process or zinc powder displacement process can exist with the heap leaching process at the same time. Because the recovery rate of the heap leaching process is lower, it can't replace CIP process for achieving good benefits in the high-grade gold separation, namely the high-grade ore is sent to the mineral processing plant or cyanide plant, and low-grade ore, submarginal ore or waste rock are treated with the heap leaching process.


 marketing@ytxinhai.com
marketing@ytxinhai.com  0086 13810327080
0086 13810327080 






































































































 CHAT
CHAT MESSAGE
MESSAGE






